LEARN MUSIC AND AUDIO PRODUCTION | Wavmonopoly TIPS AND TRICKS
What is Audio Mastering?

wavmonopoly June 8, 2022

It’s a question that musicians and producers have asked for years – what is mastering? And more importantly, what is the importance of audio mastering in music production?
Audio mastering is the final step in the recording process and often the most important. It can take an average track and make it sound professional, polished, and ready for release if done correctly. This is all done during the mastering stage. Usually, the position that handles that job is the mastering engineer. But what goes into a good mastering job?
In this article, we’ll look at what audio mastering is, what it involves, and how it can benefit your music.
What Is Mastering?
Audio Mastering is the final process in audio post-production (usually for a record and a film or documentary soundtrack). This is a key step in sound quality whose main objective is to balance the final mix and its different sound elements and optimize reproduction to achieve a professional result.
The entire mix is reviewed by a professional mastering engineer during mastering to be distributed in different formats and commercial devices (CD, vinyl, radio, video games…) or streaming services. It is a very important step that allows the cohesion of all the audio and that, in addition, enables sound uniformity between the different tracks of an album.
The main objectives of mastering would be:
- Achieve quality sound to play in different formats, devices, and platforms. Keep in mind that the volume and compression type differ a bit on digital platforms.
- Achieve a suitable and uniform volume to avoid annoying changes between songs. It would be about “giving color” and consistency to the themes so that there are no distortions between them.
What Does a Mastered Song Sound Like?
Listen to this audio example mastered with vocal presets from Wav Monopoly. What do you notice?
Hip-Hop: “CANDY” by Q. Lord Not Mastered
Hip-Hop: “CANDY” by Q. Lord Mastered
How to Master Audio?
Since it is the last step in the recording process, mastering is responsible for giving the final “polish” to a track. In general, this means ensuring that the track sounds its best when played on various devices and platforms, from radio to streaming services.
To achieve this balance, it is necessary to carry out a complex procedure in which several processes come into play: equalization, compression, limiting, soft clipping and stereo imaging.
Equalization

Equalization is adjusting the levels of different frequencies in the audio signal. We do this by using a parametric or graphic equalizer. A parametric EQ allows you to boost or cut specific frequencies, while a graphic EQ will let you adjust a range of frequencies at once.
Compression

Compression is used to even out the audio signal levels, reducing the dynamic range. There are two ways to do this: a compressor or a limiter. A compressor will reduce the dynamic range of a signal level when it goes above a certain threshold. While a limiter will completely stop the signal from getting any louder. This will control the dynamic range of the overall track. Which will allow us a more tamed dynamic range to be able to bring the level up in the limiting stage. Thus allowing us a ready audio track to make it louder.
Stereo Imaging
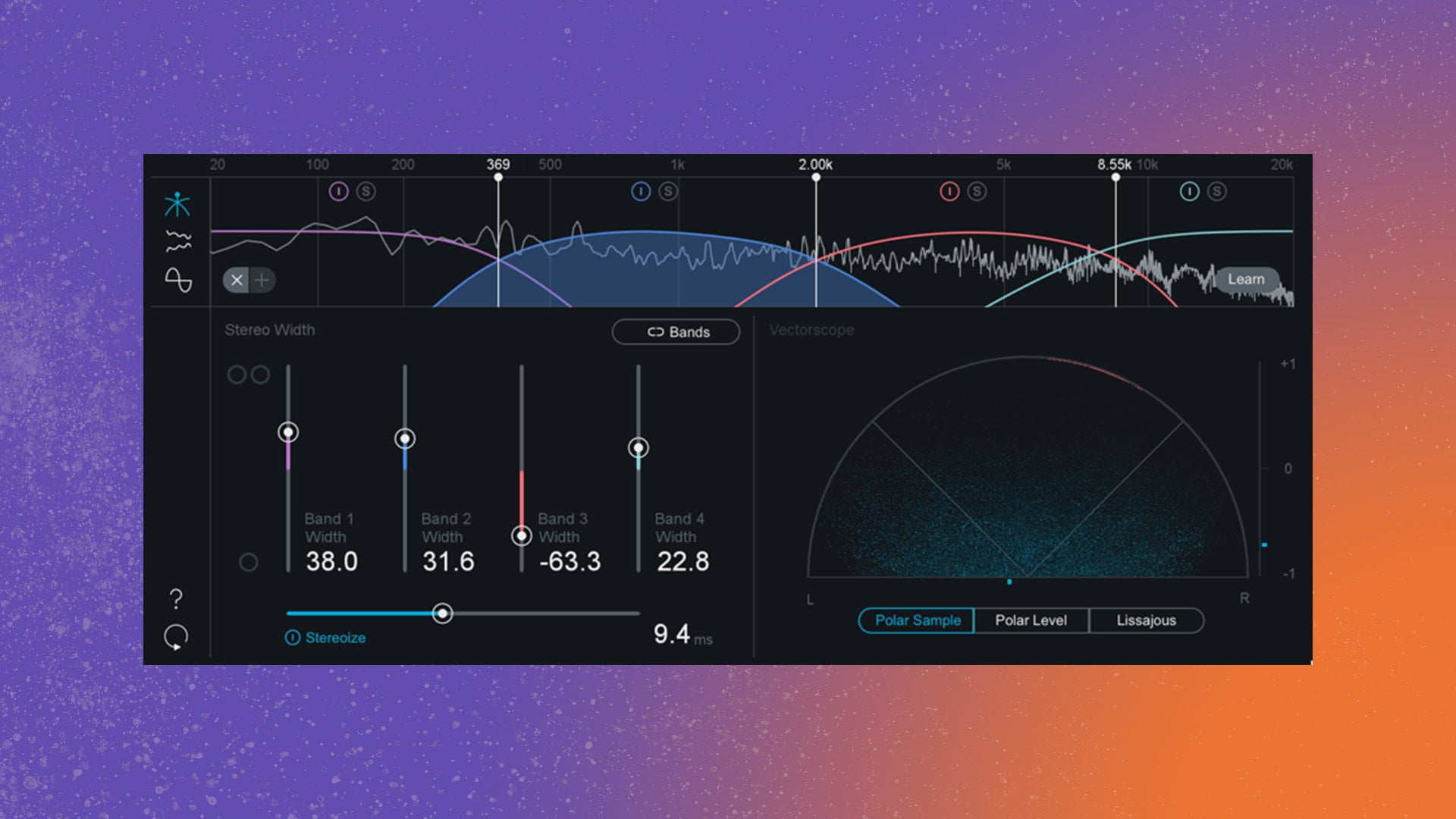
Stereo imaging is one of the most important aspects of audio mastering. It is the process of creating a stereo image of the recording. This can be achieved by manipulating the stereo field. Mastering engineers achieve this by using stereo plugins, EQs, compressors, and other effects. Stereo imaging can be used to create a wide stereo image. And also focus on the left and right sides of a particular instrument or sound. It is also possible to use stereo imaging to create a sense of depth in the recording.
Be carefully manipulating the stereo field. Sometimes it can introduce something called phasing if manipulated too much. But done at optimal levels, It is possible to create an illusion of space and depth that can make the recording sound more realistic. Stereo imaging is an essential tool for audio mastering. It greatly improve the sound of a recording and experience of the song.
Soft Clipping

A soft clipper is an audio processing tool used during the mastering phase to make a song louder. It does this by gently “clipping” the peaks of the waveform, which results in a fuller, richer sound. Soft clipping is generally considered to be more transparent than hard clipping, which can produce a harsh, distorted sound. Although soft clipping can be used to boost the overall volume of a track, it should be used sparingly, as too much clipping can cause the audio to sound muddy and cluttered. When used judiciously, however, soft clipping can give your tracks the extra oomph they need to cut through the mix and make an impact.
Limiting
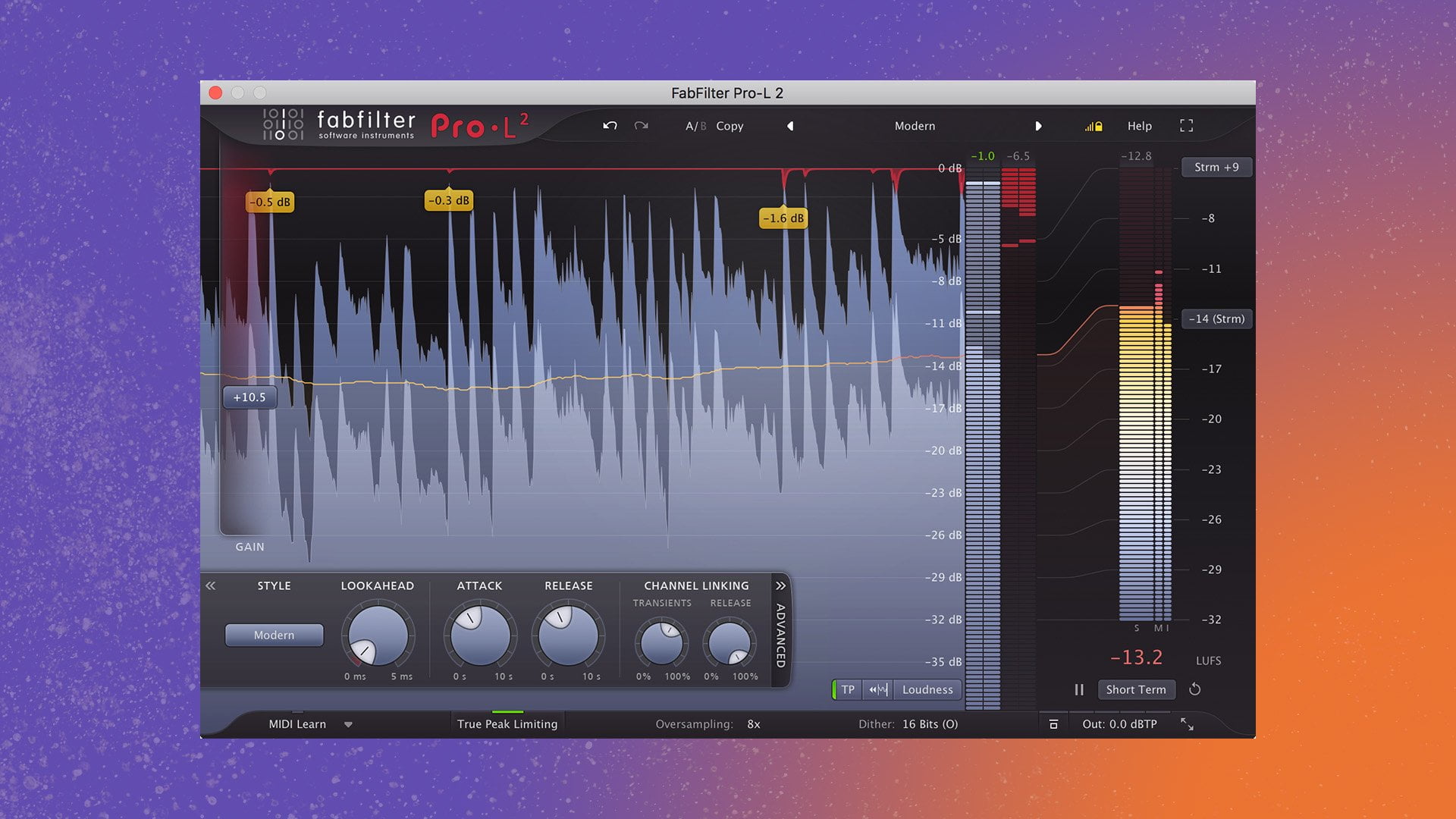
Limiting is a type of compression used to prevent the signal from getting too loud. This is accomplished by establishing a limit for the signal’s level, preventing it from ever reaching above that level.
Sequencing and Spacing
This is the last phase of mastering in which the audio is ordered and, in addition, the duration of the silences between the different songs is determined.
Types Of Mastering: Stereo vs. Stem Mastering
When it comes time to master your song, you have two choices: stereo or stem. The difference between the two mostly pertains to which elements will be used to create proper stereo enhancement of sound panned across speakers without losing any detail when played back through an amplifier/speakers. But this doesn’t mean one style can never be mixed into another.
Stereo Mastering
Stereo mastering is the process of focusing on a single digital audio file or final mix for tracks to be mastered. The goal in this method, as with any other form/stage before distribution (think vinyl record), should have stellar mixes so errors can’t get restored once they’re baked into them at hand-made speeds by humans who are not always perfectible machines themselves.
Stem Mastering
Finally, there’s stem mastering. This process takes the audio or music production one step further by applying it to each of your tracks – known as stems. The quality may not be greater than what you could achieve with just a mix, but this also allows for more collaboration between engineer and producer, leading to better starting points when trying sound out on playback equipment or completing projects in other programs.
Differences between Mixing and Mastering
Following are the key differences between mixing and mastering:
- Mixing and Mastering share some techniques and processes, but they are not the same thing. In fact, it is recommended that the audio engineers who perform the mix are different from the mastering engineer. Why? Because his ears and brain will already be “bias”. Basically, it makes it more difficult for an engineer to spot errors or making it a conflict.
- Mixing is a process before mastering in which the different instruments and audio tracks are brought together in a song; that is, the theme previously recorded by tracks is unified. In mastering the details, the volume and the themes of the same work are unified. The final result of a musical project largely depends on good or bad mastering.
What Is NOT Mastering?
- Mastering is not just putting a limit on the end of the Master Fader and turning up the volume. This is part of the process. However, proper master requires more.
- Mastering will never be able to make a bad mix sound good. That is impossible, and it will never be possible, no matter how good the master’s engineering is.
- Mastering is not about adjusting the frequency balance of certain instruments in the mix; mastering is about adjusting the frequency balance of the overall song.
Importance of Audio Mastering
In short, when you master your album, you make sure that the song one listens to doesn’t fade out of the speakers while the next one barely hears. The mixing process extends to this, but mastering takes a broader view.
Here are some compelling reasons why audio mastering is important:
- Consistent volume and level – The mastering process raises the overall level of the tracks. It does this to makes each track on the album consistent. Just imagine, listening to the entire album and you have to adjust the volume on every song. That would be very disruptive to the listener. But mastering allow a consistent volume level instead of having to adjust the level for each song. In addition, this allows music to be played from a variety of playback systems, be it a car stereo or headphones.
- Consistent sound – Especially on albums. Mastering will make tracks sound as if they were recorded and mixed at the same time and place.
- Improve music quality – As mentioned above, that is the main purpose when mastering a song or album. In this highly competitive music scene, your chances of succeeding in the music business are drastically diminished if you don’t have your music properly mastered.
- Appropriate volume levels – It’s not just about making your music loud (the loudness war is over); it’s about adapting your music to different platforms.
Tips to Master Audio
The mastering process can be very simple or quite complex, depending on the goals you have for your project. Here is a general overview of how to master music or audio:
Establish the “Aesthetic” and Sound of the Song
The first step is to listen to the mix and make sure it sounds great. You want to make sure that all the song elements are in balance and that the overall sound is pleasing.
Remember, you can always come back and adjust the mix later, but it is important to have a good starting point.
Create Consistency Across an Album
Once you have established the song’s sound, it is time to make sure that the sound is consistent across the entire album. This includes matching the levels of each track and ensuring that the overall sound is cohesive.
To do this, you will need to listen to the album as a whole and make adjustments to the levels of each track. You may also need to make some EQ adjustments to certain tracks to ensure they fit well with the rest of the album.
Prepare for Distribution
This is one of the crucial steps in the mastering process. You will need to ensure that your mastered audio tracks are ready for distribution. This includes ensuring that the tracks are of the highest quality and properly formatted for the desired distribution platform.
Another important consideration is the delivery format of your song or sequence. You have many options to choose from, depending on what you need it for, whether downloading/ manufacturing copies & duplicating them as well!
If distributing into other countries’ markets, make sure their audio standards match up perfectly before sending out anything over internet connections like Wi-Fi, etc…
For web-centered distribution, adjust the levels for online distribution to meet the requirements for conversion to MP3, AAC, or high-resolution files and attach the necessary data.
Conclusion
Post-production in the mastering stage is quite important. So we can hear the quality of the final product professionally and, above all, attractive and ear pleasing.
Mastering should have the same importance as mixing, and it is something that is often not done because it is a less laborious audio production process. However, it is more specific and delicate.
We hope this article has helped you understand more about mastering and its process!