LEARN MUSIC AND AUDIO PRODUCTION | Wavmonopoly TIPS AND TRICKS
What is Dithering and How to use it?
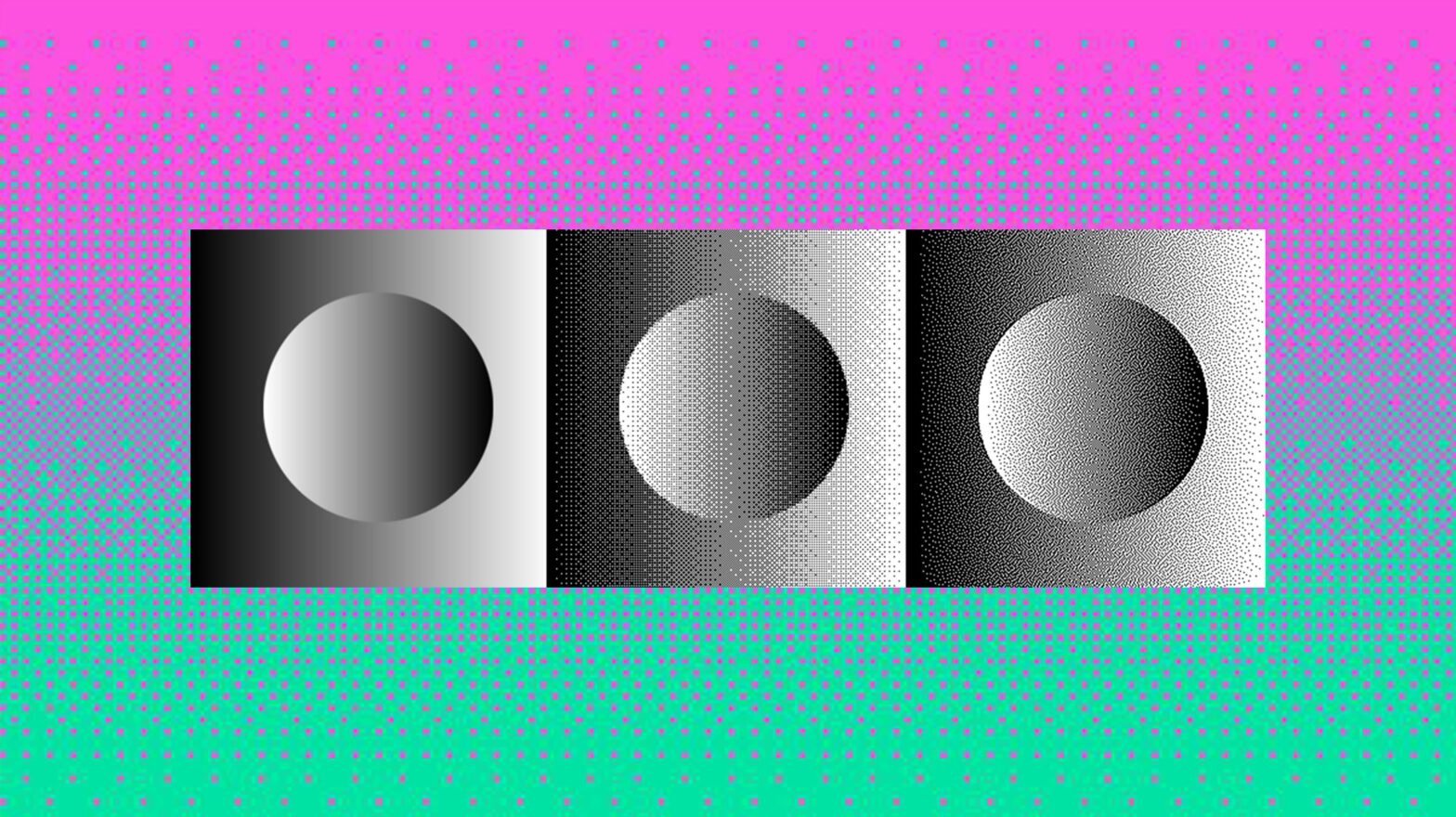
wavmonopoly August 19, 2022
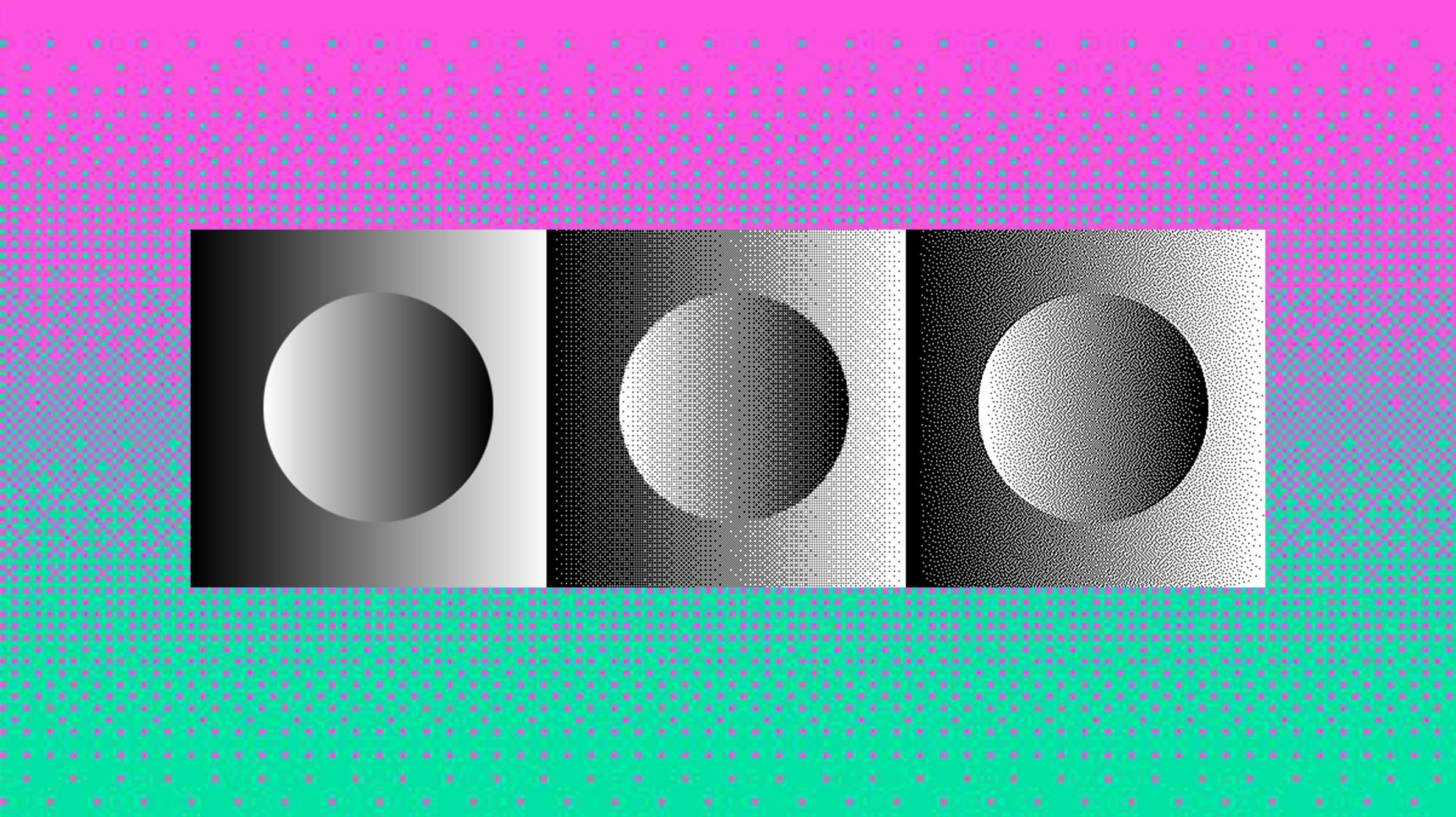
If you’re new to audio engineering, you may have heard the term “dither” or “dithering” but not know what it is or when to use it. Dither is a type of noise that is used when encoding digital audio files. It’s added in order to minimize distortion and improve the sound quality. In this blog post, we’ll take a closer look at dither and explain why and how you should use it. Stay tuned!
What exactly is dithering?
Dithering is a process of adding noise to a digital signal in order to reduce distortion. When encoding audio files, it helps to minimize quantization errors and improve sound quality. It works by creating random fluctuations in the signal that are too small to be perceived by the human ear. The result is a more natural sounding recording with less digital artifacts.
Types of Audio Dithering
There are two types of audio dithering: noise shaping and pattern dithering.
Noise Shaping
Noise shaping is a type of audio dithering that reduces the amount of audible noise by pushing it into frequencies that are inaudible to human ears. This is done by adding a very low-level signal to the audio signal before it is converted from analog to digital. The added signal has a shape that is complementary to the shapes of the quantization error components in the audible frequency range. This type of dithering is very effective at reducing quantization noise, but can also introduce other types of artifacts into the audio signal.
Pattern Dithering
Pattern dithering is a type of audio dithering that uses a fixed pattern of noise to reduce the amount of audible quantization noise. This is done by adding a very low-level noise signal to the audio signal before it is converted from analog to digital. The added noise has a fixed pattern that is designed to spread the quantization error evenly throughout the audible frequency range. This type of dithering is less effective at reducing quantization noise than noise shaping, but it does not introduce any other types of artifacts into the audio signal.
Both noise shaping and pattern dithering are effective at reducing the amount of audible quantization noise. However, they both have their own advantages and disadvantages. Noise shaping is more effective at reducing quantization noise, but can also introduce other types of artifacts into the audio signal. Pattern dithering is less effective at reducing noise, but it does not introduce any other types of artifacts into the audio signal.
Benefits of Audio Dithering
Audio dithering is the process of adding noise to a digital signal in order to improve its sound quality. Some of its benefits include:
Improves the bit-depth of digital signal
Bit depth is the number of bits used to represent each sample in an audio file. The higher the bit-depth, the more accurate the representation of the original analog signal. However, higher bit-depths also result in larger file sizes.
The standard bit-depth for CDs is 16-bits. This is considered to be sufficient for most people . However, some audiophiles prefer to use files with higher bit-depths, such as 24, or 32 bits.
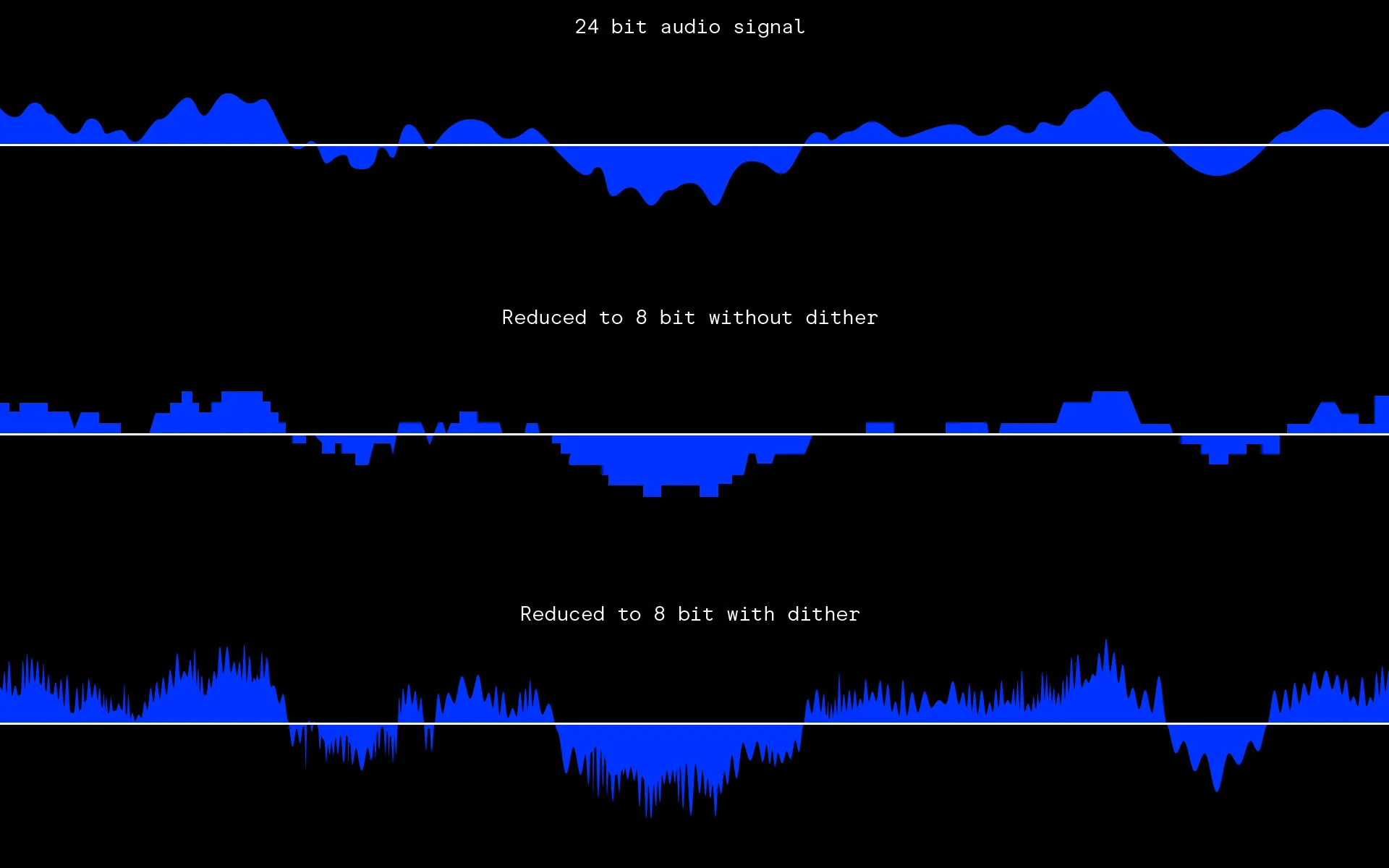
When dithering is used, the bit-depth of the audio signal is increased. This is because the added noise signal has a certain amount of bits. The number of bits in the noise signal determines the final bit-depth of the audio signal. For example, if an audio signal with a bit-depth of 16-bits is dithered with a noise signal that has a bit-depth of 8-bits, the final bit-depth of the signal will be 24-bits.
The bit-depth of an audio file can be increased by using a higher bit-depth noise signal. However, changing bit depth will also increase the file size. Therefore, it is important to choose an appropriate bit-depth for the audio signal, based on the desired trade-off between sound quality and file size.
Dithering makes digital audio sound more analog
Digital audio is typically very clean and precise. However, this can sometimes make it sound clinical or sterile. Dithering can help to give digital audio a more analog-like sound. This is because the added noise signal will mask some of the digital artifacts that can make audio sound harsh.
Some people believe that dithering makes digital audio sound warmer and more natural. Others believe that it makes audio sound smoother and more polished. Ultimately, it is up to the listener to decide whether or not it improves the sound of digital audio.
Reduces quantization noise
Quantization noise is a form of distortion that occurs when an analog signal is converted to digital. The amplitude of the quantization noise is related to the bit-depth of the digital signal. The higher the bit-depth, the lower the level of noise.
Dithering can help to reduce the level of noise by adding noise to the signal. The added noise will mask the quantization distortion, resulting in a reduction of the overall noise level.
The amount of noise that is added should be carefully chosen. If too much noise is added, it will be audible and can degrade the sound quality. However, if too little noise is added, the noise will not be sufficiently reduced.
Improves the overall sound quality of digital audio
If you are looking to improve the sound quality of your digital audio, dithering is a technique that is worth considering. It can help to reduce distortion and artifacts, and make the audio sound more natural. It can also be used to improve the dynamic range of the audio, making it easier to hear quiet sounds.
There are many different types of dithering algorithms. Each algorithm has its own unique set of characteristics. Some common types of algorithms include:
- Rectangular dithering
- Triangular dithering
- Gaussian dithering
- Shaped dithering
These algorithms can be applied in different ways, depending on the desired sound. For example, some algorithms are better at preserving the integrity of transients (sudden changes in amplitude). Others are better at minimizing distortion.
It is important to experiment with different dithering algorithms to find the one that sounds best for a particular application..
When should you use audio dithering?
There are a few different scenarios where you might want to use audio dithering. One common situation is when you’re exporting your audio project from your DAW (Digital Audio Workstation). Many DAWs have the option to apply it when exporting, and this can help reduce any unwanted digital artifacts that may occur.
Another scenario where you might want to use audio dithering is when converting between different bit depths. For example, if you’re converting from 24-bit audio to 16-bit audio, applying dithering can help minimize any degradation in sound quality.
Finally, some people like to add a touch of dither to their finished mixes just for good measure. This can give the mix a slightly warmer sound, and can help hide any minor digital imperfections that may be present.
Ultimately, whether or not you use audio dithering is up to personal preference. There’s no right or wrong answer, so just experiment and see what sounds best to you!
When should you avoid audio dithering?
Dithering is a process of adding noise to audio signals in order to mask quantization errors. However, dithering is not always the best solution. In some cases, it can actually degrade the quality of the audio signal more than helping it. Here are some situations where you should avoid using dithering:
1. When the source material is already very noisy
If the source material is already quite noisy, then adding more noise via dithering will only make matters worse. In this case, it’s better to leave the signal undithered.
2. When the quantization error is not audible
If the quantization error is not audible, then there’s no need to add noise via dithering. In this case, it’s better to leave the signal undithered.
3. When the bit depth reduction is not significant
If the bit depth reduction is not significant, then the added noise from dithering may be more noticeable than the quantization error itself. In this case, it’s better to leave the signal undithered.
4. When dithering introduces unwanted artifacts
In some cases, dithering can introduce unwanted artifacts into the audio signal. These artifacts can degrade the quality of the signal and should be avoided if possible.
How do you add dithering?
There are a few different ways to add dithering to an audio signal. The most common method is to use a plug-in or software application that offers dithering capabilities. Many popular DAWs have dithering as a built-in feature. For example, Pro Tools has a “dither” setting that can be enabled when exporting audio files. If your DAW doesn’t offer dithering, there are a number of third-party plug-ins that can be used.
Another way to add dithering is to use hardware that offers dithering capabilities. For example, some professional audio interfaces have a setting that can be enabled for dithering. Alternatively, there are stand-alone hardware units that can be used for dithering. These units typically offer more control over the dithering process, which can be helpful if you’re working with high-resolution audio files.
Finally, some digital converters offer dithering capabilities as well. This is particularly common in devices that support multiple bit depths, such as 24-bit and 32-bit converters. If your converter has a dithering setting, it’s typically enabled by default. However, you may need to check the manual to be sure.
Dithering is a valuable tool for improving sound quality and reducing distortion when encoding audio files. It’s important to understand how and when to use it in order to get the best results. Thanks for reading! We hope this blog post has been helpful.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does dithering do in audio?
Dithering is used to help reduce the quantization noise that can occur when converting between different digital audio formats. By adding a very low level of random noise to the signal, dithering can help spread the harmonic distortion over a wider frequency range, making it less audible. In many cases, dither noise can also improve the overall sound quality of the digital audio file by increasing the incoming signal-to-noise ratio. The quantization process is a key part of digital audio and dithering can be an important tool for getting the best sound quality possible.
Should I use dithering in mastering?
There is no definitive answer to this question, as it depends on the specific audio material and desired results. In general, dither audio process can be beneficial in situations where noise is likely to be audible, such as when converting between high-resolution digital audio formats or when working with very quiet sounds.
However, dithering may not be necessary or desirable in other situations, such as when converting between lower-resolution formats or when the audio is already very loud. Ultimately, it is up to the engineer or producer to decide whether or not to use it in any given situation.
Is dithering good or bad?
There is no simple answer to this question as it depends on the specific situation. In general, dithering can be beneficial in situations where quantization noise is likely to be audible, such as when converting between high-resolution digital audio formats or when working with very quiet sounds. However, it may not be necessary or desirable in other situations , such as when converting between lower-resolution formats or when the audio is already very loud. Ultimately, it is up to the engineer or producer to decide whether or not to use it in any given situation.
What is dithering in digital audio?
Dithering is the process of adding random noise to an audio signal in order to reduce quantization noise. Quantization noise is the distortion that occurs when an analog signal is converted to a digital signal with fewer bits, and it sounds like a hissing or buzzing sound. Dithering can help to mask this noise so that it is less noticeable.
There are several different types of dithering algorithms that can be used, and the choice of algorithm can have a significant impact on the sound quality of the final signal. Some dithering algorithms are better at preserving the original sound of the signal, while others may introduce unwanted artifacts. It is important to experiment with different algorithms to find the one that sounds best for your particular application.
In general, dithering is only effective when working with signals that have a low signal-to-noise ratio. For example, if you are trying to reduce the noise of a digital audio recording, it will be more effective to dither the signal before it is converted to a digital format. Once the signal has been converted to digital, it is not possible to add dithering noise back in without also introducing other types of distortion.